Labels on Alcohol Bottles Increase Awareness of Drinking Harms, Guidelines
PISCATAWAY, N.J., May 4, 2020 (Newswire.com) - When alcohol bottles come with conspicuous labels providing information on the risks of alcohol consumption or drinking guidelines, people are better informed about alcohol’s harms and may cut down their drinking, according to a series of studies in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
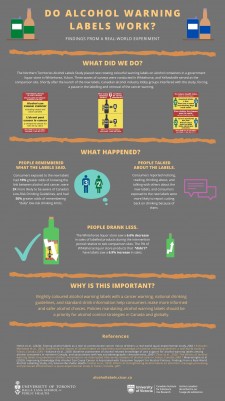
“The results provide the first real-world evidence that relatively large, bright yellow alcohol labels with rotating health messages get noticed by consumers and can increase awareness of national drinking guidelines, improve knowledge of alcohol-related health risks, such as cancer, and reduce alcohol sales compared to control sites without the labels,” says Erin Hobin, Ph.D., of the University of Toronto’s Dalla Lana School of Public Health, and principal investigator on the studies in this series.
The Canadian research, called the Northern Territories Alcohol Label Study, involved placing bright-colored labels on bottles of beer, wine and liquor with one of three messages: one about the scientific evidence regarding the link between alcohol and cancer, a second with the Canadian government’s low-risk drinking guidelines and a third with information about the number of standard drinks in the container.
One of the studies found that adding such labels to alcohol bottles (300,000 labels in all) decreased total sales of alcohol by 6.9% compared with sales in regions without the new labels.
In another article, among 2,049 participants, awareness of Canada’s low-risk drinking guidelines increased nearly three times in the site in which the labels were placed compared with a control location. (Canada recommends no more than two drinks a day for women, no more than three for men and at least two alcohol-free days per week.)
A third study generated controversy. Here, Hobin and colleagues queried the same 2,049 participants about their knowledge of the link between alcohol consumption and cancer.
Before the study, roughly 25% of participants knew alcohol consumption can cause cancer. After the labeling, awareness in Yukon rose to 42%, a 10% greater increase in awareness of the alcohol-cancer link relative to the control site in neighboring Northwest Territories.
However, the cancer label part of these studies was cut short because the alcohol industry protested. The industry complained that the Yukon Government, who helped coordinate the study and is responsible for alcohol distribution and sales in the territory, did not have legal authority to place such labels, that the labels violated industry’s freedom of expression and that the government was defaming alcohol manufacturers.
Under pressure, the Yukon Government shut down the cancer label research in December 2017, only one month after the study’s launch.
After consultation with legal experts, the researchers conclude, “none of the industry’s claims had any merit.” In fact, they note that provincial and territorial governments in Canada could be held liable if they do not warn consumers about the link between alcohol and cancer. (The World Health Organization declared alcohol a human carcinogen over 30 years ago.)
Media contact:
Nicole Bodnar
289-259-5080
nicole.bodnar@utoronto.ca
Source: Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs
